A* Algorithm
On every iteration through the main loop the code finds the unvisited cell with the smallest distance value, i.e, the node that is the closest to the start node.
function [route,numExpanded] = AStarGrid (input_map, start_coords, dest_coords)
% Run A* algorithm on a grid.
% Inputs :
% input_map : a logical array where the freespace cells are false or 0 and
% the obstacles are true or 1
% start_coords and dest_coords : Coordinates of the start and end cell
% respectively, the first entry is the row and the second the column.
% Output :
% route : An array containing the linear indices of the cells along the
% shortest route from start to dest or an empty array if there is no
% route. This is a single dimensional vector
% numExpanded: Remember to also return the total number of nodes
% expanded during your search. Do not count the goal node as an expanded node.
% set up color map for display
% 1 - white - clear cell
% 2 - black - obstacle
% 3 - red = visited
% 4 - blue - on list
% 5 - green - start
% 6 - yellow - destination
cmap = [1 1 1; ...
0 0 0; ...
1 0 0; ...
0 0 1; ...
0 1 0; ...
1 1 0; ...
0.5 0.5 0.5];
colormap(cmap);
% variable to control if the map is being visualized on every
% iteration
drawMapEveryTime = true;
[nrows, ncols] = size(input_map);
% map - a table that keeps track of the state of each grid cell
map = zeros(nrows,ncols);
map(~input_map) = 1; % Mark free cells
map(input_map) = 2; % Mark obstacle cells
% Generate linear indices of start and dest nodes
start_node = sub2ind(size(map), start_coords(1), start_coords(2));
dest_node = sub2ind(size(map), dest_coords(1), dest_coords(2));
map(start_node) = 5;
map(dest_node) = 6;
% meshgrid will `replicate grid vectors' nrows and ncols to produce
% a full grid
% type `help meshgrid' in the Matlab command prompt for more information
parent = zeros(nrows,ncols);
%
[X, Y] = meshgrid (1:ncols, 1:nrows);
xd = dest_coords(1);
yd = dest_coords(2);
% Evaluate Heuristic function, H, for each grid cell
% Manhattan distance
H = abs(X - xd) + abs(Y - yd);
H = H';
% Initialize cost arrays
f = Inf(nrows,ncols);
g = Inf(nrows,ncols);
g(start_node) = 0;
f(start_node) = H(start_node);
% keep track of the number of nodes that are expanded
numExpanded = 0;
% Main Loop
while true
% Draw current map
map(start_node) = 5;
map(dest_node) = 6;
% make drawMapEveryTime = true if you want to see how the
% nodes are expanded on the grid.
if (drawMapEveryTime)
image(1.5, 1.5, map);
grid on;
axis image;
drawnow;
end
% Find the node with the minimum f value
[min_f, current] = min(f(:));
if ((current == dest_node) || isinf(min_f))
break;
end;
% Update input_map
map(current) = 3;
f(current) = Inf; % remove this node from further consideration
% Compute row, column coordinates of current node
[i, j] = ind2sub(size(f), current);
% *********************************************************************
% ALL YOUR CODE BETWEEN THESE LINES OF STARS
% Visit all of the neighbors around the current node and update the
% entries in the map, f, g and parent arrays
%
numExpanded = numExpanded + 1;
currentNode = [i,j];
% This is for putting the nodes around the starting node
upNode = [i+1,j];
downNode = [i-1,j];
leftNode = [i,j-1];
rightNode = [i,j+1];
% For the neighbors
neighbours = [upNode; downNode; leftNode; rightNode];
for n = 1:4
% checks boundaries
if (neighbours(n,1)>0 && neighbours(n,2)>0) && (neighbours(n,1)<= nrows && neighbours(n,2)<=ncols)
% checks positions 1- white 2-obstacle 3-visited 4-onlist
% 5-start 6-destination if the position is not an obstacle,
% visited or the start or if it's destination, then calculate
if( map(neighbours(n,1),neighbours(n,2)) ~= 2 && map(neighbours(n,1),neighbours(n,2)) ~= 3 && ...
map(neighbours(n,1),neighbours(n,2)) ~= 5 || map(neighbours(n,1),neighbours(n,2)) == 6)
% adds to list and calculates distance to nodes
if(g(neighbours(n,1),neighbours(n,2)) > 1 + sum(abs(start_coords - currentNode)) || map(neighbours(n,1),neighbours(n,2)) == 6)
map(neighbours(n,1),neighbours(n,2)) = 4; % adds to list of expansion
g(neighbours(n,1),neighbours(n,2)) = 1 + sum(abs(start_coords-currentNode));
f(neighbours(n,1),neighbours(n,2)) = g(neighbours(n,1),neighbours(n,2)) + H(neighbours(n,1),neighbours(n,2));
parent(neighbours(n,1),neighbours(n,2)) = sub2ind(size(map),current);
end
end
end
end
%*********************************************************************
end
%% Construct route from start to dest by following the parent links
if (isinf(f(dest_node)))
route = [];
else
route = [dest_node];
while (parent(route(1)) ~= 0)
route = [parent(route(1)), route];
end
% Snippet of code used to visualize the map and the path
for k = 2:length(route) - 1
map(route(k)) = 7;
pause(0.1);
image(1.5, 1.5, map);
grid on;
axis image;
end
end
end
A* Test 10x10
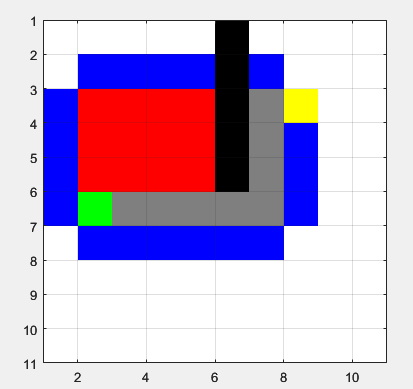
A* Test 25x25
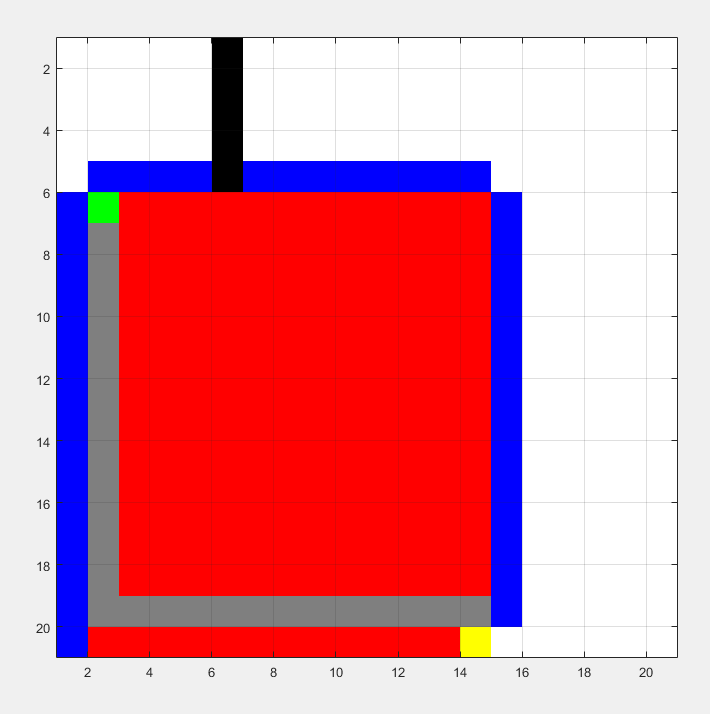
PREVIOUSEye tracking analysis